followthethings.com
Fashion | Health & Beauty
“Jamelia: Whose Hair Is It Anyway?“
A TV documentary film fronted by Jamelia, directed by Jo Hughes, produced by Morgan Matthews for Minnow Films.
Slideshow of documentary stills embedded above. BBC iPlayer page here. Watch on Box of Broadcasts (with institutional login) here.
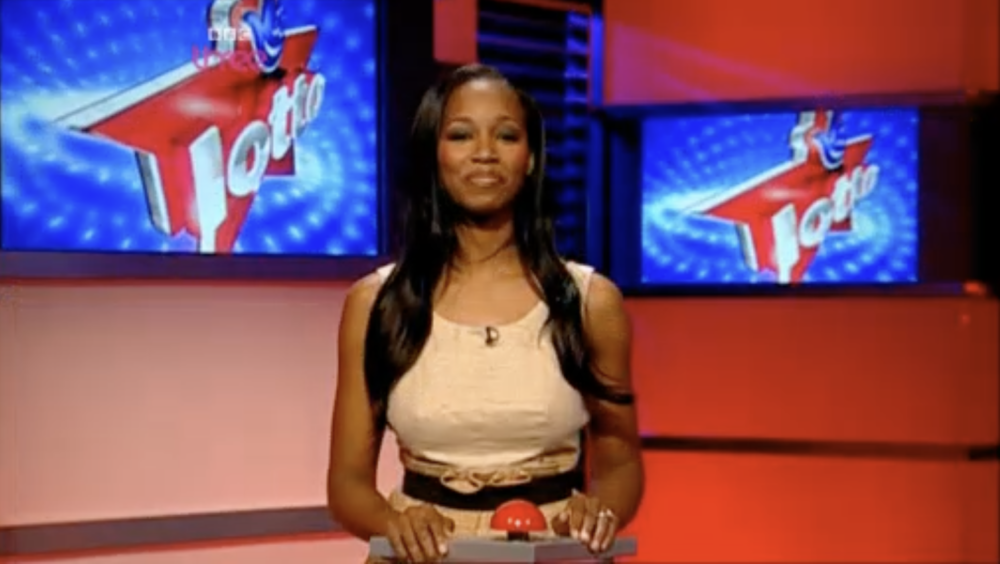
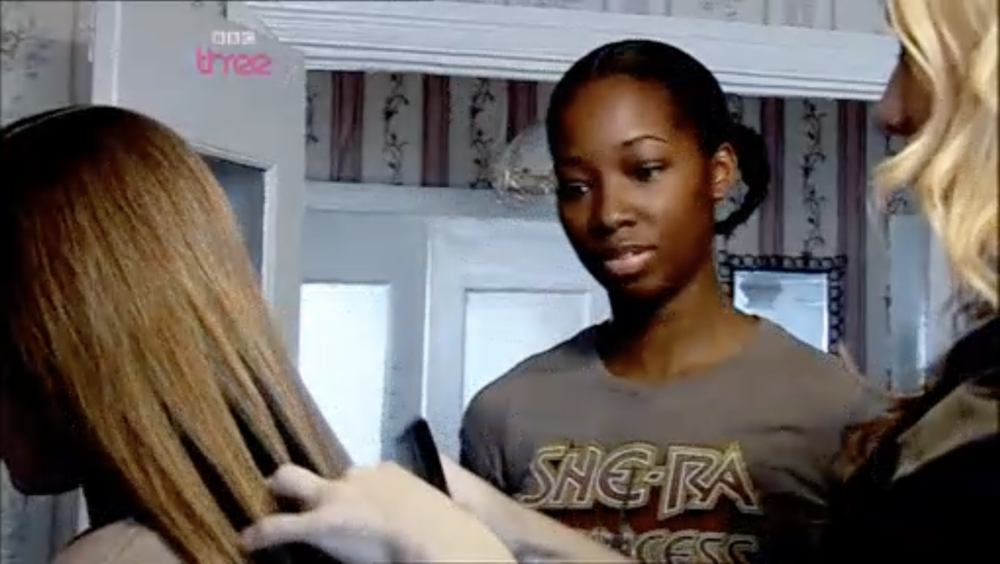
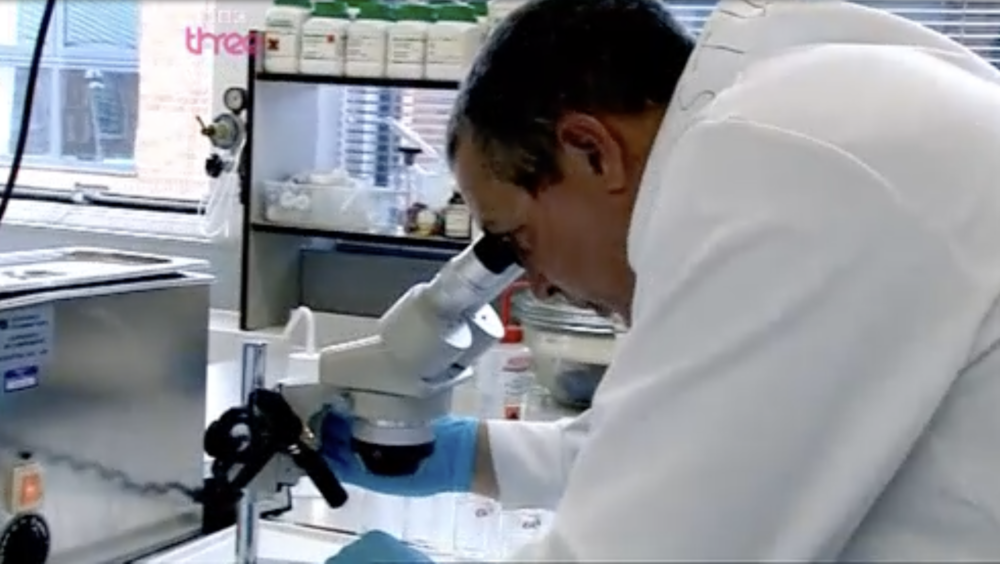
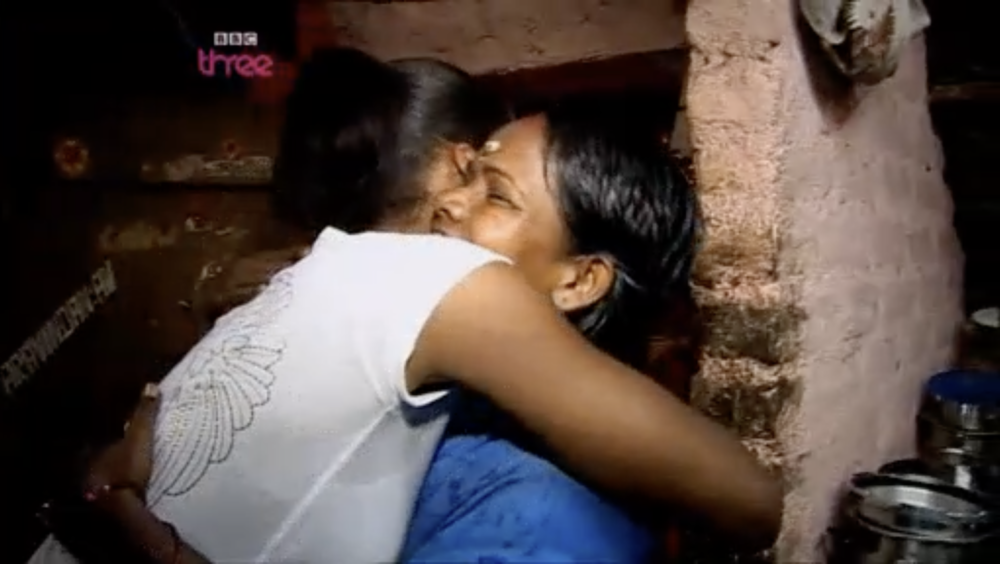
This is the example that inspired the first version of followthethings.com – an online list of ‘follow the things’ resources. In this TV documentary, legendary Birmingham pop singer Jamelia – best known for her 2010 song ‘Superstar’ – wants to find out about a hair extension that she wore on TV to present a National Lottery draw. It’s real human hair. Straight, long and black. But whose hair was it originally? Whose hair was she wearing? She asks some young women at a local school about where their extensions come from. They don’t know. Dead people? With the help of hair traders and a forensic scientist, she travels along human hair’s supply chains to find out if that’s true. First, she travels to Russia with a Russian hair trader. They drive to a village to buy the long and untreated hair of teenage girls (like Tatiana in the photo above). Their hair is worth a lot of money. Next, getting her hair forensically analysed in a lab provides some clues about its geographical origin. So, she travels to India, to the city of Chennai, and finds a woman whose hair she is convinced it originally was. But she hadn’t sold it. It had been shaved off at a temple, and the temple had sold it on. The money they made was used to feed the poor. So this isn’t a story of exploitation along supply chains that you might expect to find. Jamelia and the woman whose hair she probably wore bond over being mothers of daughters. The documentary turns into a kind of a reunion of long lost relations. This story has a happy ending and many of the people who comment on the film are suspicious of that. What have Jamelia and the film company brushed under the carpet? Do these following films always have to end up with depressing conclusions and appeals to consumers to do something for poor and powerless producers? A lot of the commentary is also about Jamelia and whether she is boycotting real hair now (like she allegedly said, or didn’t) or is a ‘hypocrite’ (that’s a criticism to expect of every example on this site). But there’s a final twist in this tale, that comes to the surface many years later. It’s a shocking example of a film like this making an impact. An important customer-base for Indian temple-sourced hair stops buying it. Because of a BBC documentary about the hair trade. It seems to be this one. Read on.
Page reference: Ian Cook et al (2020) Jamelia: Whose Hair Is It Anyway? followthethings.com/jamelia-who-hair-is-it-anyway.shtml (last accessed <insert date here>)
Estimated reading time: 47 minutes.
Continue reading Jamelia: Whose Hair Is It Anyway? ![]()